First, selection and installation of valves.
1. Principles of valve selection for water supply pipelines.
- The block valve shall be used in pipelines with a diameter less than 50mm. While the gate valve and the butterfly valve shall be used for ones with a diameter more than 50mm.
- The control valve and the block valve shall be used in need of volume and pressure regulation.
- The gate valve shall be used in request of the low resistance (like the pump suction pipe).
- The gate valve and the butterfly valve shall be used for the commuted flow. Never is it the case for the block valve.
- The butterfly valve and the ball valve can be applied to limited installation space.
- The block valve shall be used for the pipeline frequently switched on-and-off.
- The multi-function valve shall be used for the outlet pipe of large caliber water pumps.
2. Parts of the water supply pipeline shall be provided with valves.
- The inlet pipe between residential quarters and the municipal water supply.
- Long pipes. The residential outdoor ring pipe network shall be set node according to the separation requirements. Valves shall be provided to separate into the short.
- The head of branch pipes and household pipes connected the main water supply pipe in the residential quarter.
- Inlet pipes, water meters and branch standpipes (the bottom of standpipe and the two ends of vertical loop standpipe).
- Branch pipes of ring pipe network and connecting pipes of branch pipe network.
- The head of the distribution pipes of the indoor water supply, like households, public toilets, etc. Valve should be provided in the case of 3 or more distribution points.
- The outlet pipe of the pump and the suction of the self priming pump.
- The inlet, the outlet and drain pipes of the water tank.
- The inlet supply pipes for equipment (like heaters, coolers, etc.).
- Water distribution pipes for sanitary appliances such as urinals, toilets, washbasins, showers, etc. .
- Some accessories. For example, valves shall be installed in front of the automatic exhaust valve, pressure relief valve, water hammer eliminator, pressure gauge, sprinkler and at both ends of the relief valve and the back-flow preventer.
- The lowest part of the water distribution system. Drain valves here is a better choice.
3. Factors of check valve selection are its installation site, the upstream pressure, sealing requirement, the hydraulic ram size and so on.
- Low upstream pressure. Swing, ball and shuttle check valves are preferable.
- An excellent sealing performance requested. Spring check valves are preferable.
- The weakened hydraulic ram. Quick-closing silent check valves or damping closure-delayed check valves are preferable.
- A self-closing flap or spool by gravity or spring.
4. Sections of the water supply pipeline should be provided with check valves.
Sections are the leading-in pipes, inlet pipes of sealed water heaters or water equipment and outlet pipes of the water pump, one-way cisterns, water towers, or upland cisterns.
Note: No check valve for pipe sections with a back-flow preventer.
5. Sections of the water supply pipeline shall be equipped with exhaust devices.
- The end and the highest point of the intermittent pipe network shall be equipped with automatic exhaust valves.
- The peak point of the pipe section with obvious air inflation shall be equipped with automatic exhaust valves or manual valves.
- The highest point of he water distribution network with air pressure water supply devices shall be equipped with automatic exhaust valves in the case of automatic supply pressure tank.
Second, merits and drawbacks of various valves:
1. The Gate Valve:
The gate valve is a valve whose closing part (the gate) moves vertically along the axis of the passage.It is mainly used for blocking medium in the pipeline, that is, being a wide open or a sealed close, it generally can not be used as a throttle. It can be applied to extreme temperature and pressure based on the valve material, except mud pipelines and the like.
Advantages of Gate Valves
- ①Minor fluid resistance.
- ② Less torque required for on-and-off.
- ③ Non-restricted medium flow in the circular network pipelines.
- ④ Less erosion of the sealing surface by medium than that of the block valve.
- ⑤Simple structures with excellent technique.
- ⑥ Shorter structure length.
Disadvantages of Gate Valves
- ①More installation space needed for its size and opening height.
- ② Relative friction of sealing surfaces. They will be worse scratched under high temperature.
- ③ Difficulties in processing, grinding and maintenance of two sealing surfaces.
- ④ Long time required for on-and-off.
2. The Butterfly Valve:
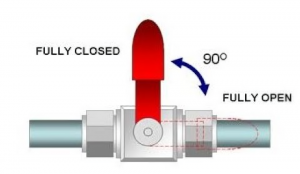
The butterfly valve is a flow regulated valve with disc pieces rotating back and forth about 90° to control its on-and-off.
Advantages of Butterfly Valves
- ①Simple structures, miniature size, light weight and less consumption. Never for large-diameter valves.
- ②A quick switch with minor fluid resistance.
- ③ Plenty applications. It can be used for media with suspended solid particles, powder and particulates referring to the strength of the sealing surface. It is perfect for two-way flow regulating of ventilation pipelines. Therefore, it is widely used in gas pipeline and water channels of metallurgy, light industry, electric, petrochemical system, etc. .
Disadvantages of Butterfly Valves
- ①Narrow regulatory range. With 30% opened, it runs more than 95% of the flow.
- ②Limited temperature and pressure conditions. Due to its structure and confined sealing material, it can not be used in pipeline systems of high temperature and high pressure. Its general working conditions is below 300 °C and PN40.
- ③ Inferior sealing performance as to the ball valve and the block valve. It can be applied to pipes of low sealing requirements.
3. The Ball Valve:
The ball valve evolved from the plug valve is a ball switched one with the ball rotating 90° to achieve its on-and-off. The ball valve is mainly used to disconnect, distribute and direct the medium flow in the pipeline and it is an excellent regulator for its V-shape opening.
Advantages of Ball Valves
- ①Minimum flow resistance (Actually is 0).
- ② Reliable applications in corrosive media and low boiling point liquids. It never tends to get stuck ( even without lubricant).
- ③ An excellent sealing performance under a wide range of pressure and temperature.
- ④ Rapid on-and-off without impact. Some structures, of which the switch time of is only 0.05 ~ 0.1 s, can be used in the automation system of the test bench.
- ⑤ An automatic location ability at the boundary position of the ball switch.
- ⑥ Two-way sealed media.
- ⑦ Isolated ball body and sealing surface of the seat from media. No erosion caused by the high-speed media rush will happen to the sealing surface during its on-and-off.
- ⑧ A compact structure of light weight. It is a best choice for low-temperature medium systems.
- ⑨ A symmetry welded body structure. It can bear the stress from the pipeline.
- ⑩ A high-differential bearing ability of the switch parts. ⑾ An overall welded body. It can be directly buried without etching internals and therefore its maximum service life is up to 30 years, which make it an ideal one for oil and natural gas pipelines.
Disadvantages of Ball Valves
- ①The Teflon sealing ring. Advantaged with minor friction coefficient, stable characteristic, anti-aging ability, wide temperature application and excellent sealing performance, it is inert to almost all chemicals. However, its physical properties is difficult to deal with. Disadvantaged with high coefficient of expansion, sensitivity to cold flow and poor thermal conductivity, the sealing surface should be constructed in consider of all these difficulties. Therefore, the harder it becomes, the less the sealing reliability is. Furthermore, the Teflon can not withstand a high temperature thus only be used below 180 °C. Otherwise, it will age. For a long-term use, 120 °C is recommended.
- ② Inferior regulation performance to the block valve, especially to the pneumatic valve (or electric valve).
4. The Block Valve:
The block valve is a valve of which the switch device (the disc) moves along the center line of the seat. As a result of the motion trail, the size of the seat opening is proportional to the disc stroke. The direct proportion, together with its relatively short stroke and reliable disconnect ability, enables it to be a good flow regulator. Therefore, the block valve is very versatile in disconnecting, regulating and throttling.
Advantages of Block Valves
- ①Wear-resistance. There is less friction between the disc and the sealing surface of the body than that of the gate valve.
- ② A shorter opening height than that of the gate valve. It is only 1 / 4 of the seat passage.
- ③ Only one sealing surface on the body and the disc. Therefore, it is easy made and convenient to repair.
- ④ The high temperature withstand ability. Its filler, which is generally a mixture of asbestos and graphite enables it to be a valve for general steam pipelines.
Disadvantages of Block Valves
- ①High flow resistance. Even its minimum resistance is greater than that of most others due to the direction change of media flow inside.
- ② A slow switch-on based on the long stroke.
5. The Plug Valve:
The plug valve refers to a rotary valve with a plunger-shaped switch. By 90°rotation, it connects or separates the channels of the plug and the valve body to achieve the om-and-off. The plug can be cylindrical or conical in shape. Being similar to each other, the ball valve is evolved from the plug valve, which is mainly used in oil field production and petrochemical industry.
6. The Safety Valve:
The safety valve refers to an over-pressure protection valve on the pressure vessels, equipment or pipelines. For a safe operation, the valve automatically opens to discharge and closes to reserve when the pressure in the equipment, container or pipeline is out of the allowable value.
7. The Steam Trap:
The steam trap is a drain device for the transmission of steam, compressed air or others, in which generates useless condensed water. It ensures the efficiency and safety of the system by timely discharging the harmful media.
It has the following functions.
- ① Quickly drain the condensed water.
- ② Seal the steam.
- ③ Remove air or other non-condensable gas.
8. The Pressure Relief Valve:
The pressure relief valve is an adjustment valve, that is, the inlet pressure is reduced by it to a certain needed outlet pressure. Supported by the energy of the medium itself, the outlet pressure is automatically stable.
9. The Check Valve:
It is also known as the back-flow valve, the check valve, the back pressure valve, the one-way valve and an automatic one for it is forced by the flow of the medium itself in the pipeline to be switched on-and-off. The check valve is used in piping systems to prevent reversed media flow, rotation pumps and drive motors, and to discharge media in the container. It can also be used for supply lines of secondary systems in which the pressure may rise above the system pressure. The check valve can be sorted into swing ones (rotation by the gravity) and lift ones (motion along the axis).